On October 31, 1921, the United States faced growing concerns over the state of its forests and the need for conservation efforts. This date marked an important milestone in the country's environmental history, as it reflected a growing recognition of the value and importance of preserving and managing forests for future generations.
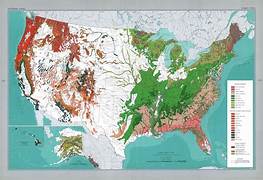
During the early 20th century, the United States experienced significant deforestation due to logging, land clearing for agriculture, and urbanization. This rapid loss of forest cover raised alarm bells among conservationists, scientists, and policymakers who recognized the vital role that forests play in maintaining ecological balance, providing resources, and supporting various wildlife species.
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, President Theodore Roosevelt, a passionate advocate for conservation, took significant steps to address the issue. In 1905, he established the United States Forest Service, an agency dedicated to the management and preservation of the country's forests. The Forest Service was tasked with overseeing the sustainable use of forest resources, conducting research, and implementing conservation practices.
By 1921, the United States Forest Service had made significant progress in its conservation efforts. It had established national forests, implemented forest management plans, and promoted sustainable logging practices. The agency also played a crucial role in fire suppression and reforestation, recognizing the importance of maintaining healthy forest ecosystems.
On October 31, 1921, the nation's attention was drawn to the importance of forests through various initiatives and events. Schools, community organizations, and government agencies organized educational programs and public awareness campaigns to highlight the value of forests and the need for their conservation. This date served as a reminder that forests are not just a collection of trees but rather complex ecosystems that provide numerous benefits to society.
The efforts to protect and manage forests continued beyond 1921. In subsequent years, the United States enacted legislation to further strengthen forest conservation. The Weeks Act of 1911 allowed the federal government to purchase private lands to protect watersheds and establish national forests in the eastern United States. The Multiple Use-Sustained Yield Act of 1960 emphasized the importance of managing forests for a range of purposes, including timber production, wildlife habitat, and recreational opportunities.
Today, the United States continues to face challenges in forest conservation, including deforestation, invasive species, and the impacts of climate change. However, the recognition of the value of forests and the importance of their conservation has only grown. Efforts are being made to promote sustainable forestry practices, protect endangered species, and restore degraded forest ecosystems.